A huge health burden
Some facts about tobacco consumption menace in India:
- 27 per cent of tobacco consumers in India fall in the 15-24 year age bracket
- If the global tobacco-related mortality is about 5.5 million people annually, India’s burden alone is nearly one million.
- With nearly 35 per cent of the adult population in the country addicted to the dangerous substance rolled in paper or leaf or packed in plastic sachets, India is the second largest consumer of tobacco products in the world.
Now the usual reason given for not curbing sales of tbacco related products is that significant revenue is raised through its sale. But what is not considered is the amount of money spent in health care due to this. This becomes relevant from the fact:
The out-of-pocket expenditure on medical treatment results in “higher poverty rates.” A recently released Health Ministry report estimates that 9.3 lakh people in India are affected by the health costs of tobacco. According to the report, the total health expenditure burden of tobacco in the year 2011 was a little over Rs.100,000 crore. To put it in perspective, the amount was “12 per cent more than the combined State and central government expenditure on health in 2011-12.”
The revenue earned through excise duty in the same year was a paltry 17 per cent of the health burden of tobacco.
Now how to curb this menace one major solution is Raising taxes:
New Union Health Minister “supports” higher taxes on cigarettes and tobacco products; raising tax on tobacco is the WHO’s theme this year. But for any tax increase to become effective, the price difference between various brands and different tobacco products must be minimal. But India follows a bizarre, producer-friendly excise duty structure for cigarettes, beedis and chewing tobacco that makes a mockery of taxation. Hence, a complete overhaul of the taxation system is warranted to achieve the desired benefits.
PM briefed on nuclear command chain
The briefing on India’s most closely held secrets was given by outgoing NSA Shiv Shankar Menon and Strategic Forces Command chief Vice-Admiral P.S. Cheema.
Naresh Chandra Committee on national security reforms had called for operational control of the arsenal to be given to a full-time chairman of the joint chiefs of staff committee, or the CJSOC, a four-star officer with a two-year tenure drawn by rotation from the three armed forces.
India's Nuclear Command and Control structure
- At the apex is Nuclear Command Authority (NCA) chaired by PM. It has a Political and Executive council. The Executive Council, chaired by the NSA gives the inputs to the Political Council, which authorises a nuclear attack when deemed necessary.
- The Political Council consiste of Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS),chaired by the PM, and advised by the Executive Council. This mechanism was implemented to ensure that Indian nukes remain firmly in civilian control and that there exists a sophisticated Command and Control mechanism to prevent their accidental or unauthorised use.
- NCA has control of the country’s estimated 90-110 nuclear warheads. In the event of a crisis, the NCA orders the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) to ready the arsenal and operationalise its directives.
- The SFC is tasked to mate the warheads with air and missile-delivery platforms held by the three armed forces.
However, the CJSOC position now goes to the senior-most of the three service chiefs, leading to changes in just a few months sometimes — which, the Naresh Chandra Committee said in its classified 2011 report, created a weak link in the command chain.
Committee felt that the CJSOC must not have the operational command of any defence force as during a nuclear crisis it might become unmanageable for him to command both the SFC and armed forces.
India is unique in this gap among nuclear-weapons States.
A GoM in Vajpayee govt recommended the appointment of a Chief of Defence Staff, a supreme military office that exists in other nuclear weapons States. The then PM, Atal Bihari Vajpayee, however, shelved the idea after resistance from politicians wary of creating a single-point military leadership as well as the air force.
INS Arihant propels India to elite club
India’s first indigenously built nuclear submarine powered by an 83 MW uranium reactor.
The submarine is capable of lurking effectively undetectable at depth almost indefinitely, as long as there is food for its 110-man crew.
INS Arihant will get the nuclear missiles it is designed to carry by early 2015.
India will join a club of just six nations with nuclear submarines carrying ballistic missiles. This would complete India’s Nuclear triad and will provide assured second strike capability.
Nuclear challenge
In March, the DRDO conducted the first test of the K-4 missile —capable of delivering a two-tonne nuclear warhead on targets up to 3,000 kilometres away.
K-4 will ensure that the country has what experts call an assured second-strike capability — the capacity to ensure retaliation even if the rest of the arsenal is wiped out in a surprise first-strike. India plans to operate three nuclear submarines with four K-4 missiles on each.
A doctrinal headache
For more than a decade now, India has kept warheads separate from the missiles that carry them, in an effort to prevent accidents or unauthorised use. Similar strategy is followed by Pakistan.
In times of crisis — like the 2001-02 standoff with Pakistan — delivery platforms and warheads have been brought together, but even then they were not mated or joined together for delivery.
But a nuclear submarine is bound to carry warheads as well as missiles. This raises significant issues of control, which need to be worked out.
Moreover, nuclear submarines can lose contact with their bases — and officers must decide if this has happened because of technical problems, or because their nation has been obliterated.
"In 1961, the Soviet submarine B-59 almost fired a 10-kilotonne warhead at the U.S. Flotilla believing that war had broken out."
Tamil Nadu presents its case
U.S. security plan for eastern Europe
President Barack Obama on Tuesday unveiled a $1 billion U.S. security plan for eastern Europe aimed at allaying fears over a resurgent Kremlin and the escalating pro-Russian uprising in ex-Soviet Ukraine.Eastern European countries fear that the Kremlin will reassert its Cold War-era grip over a large swathe of Europe following its seizure of Ukraine’s Crimea peninsula in March.
To allay these fears, Obama said, “Our commitment to Poland’s security as well as the security of our allies in central and eastern Europe is a cornerstone of our own security and it is sacrosanct,”
European Reassurance Initiative
The U.S. President then proposed an initiative of up to $1 billion to finance extra U.S. troop and military deployments to “new allies” in eastern Europe.
The historic plan that must be approved by Congress — would also build the capacity of non-NATO states such as Ukraine and Georgia to work with the United States and the Western alliance and build their own defences.
Crackdown in China ahead of Tiananmen anniversary
China has moved to muzzle any debate ahead of the 25th anniversary of the crackdown of the "1989 pro-democracy protests" at Tiananmen Square, detaining several dozen activists and scholars, imposing restrictions on universities, tightening censorship restrictions and boosting security deployments in the heart of the capital.In 25 years since the Tiananmen Square crackdown, China has indeed seen breakneck economic growth and unprecedented prosperity, as millions have been lifted out of poverty. Yet the CPC still does not allow any discussion or debate about the events.
Tiananmen Square, 1989
On the night of June 3, 1989, hundreds were killed as the Communist Party of China (CPC) under then leader Deng Xiaoping crushed the student protests by declaring martial law and sending in the Army (PLA) to clear the square. Hundreds of ordinary Beijing residents, who had come out to support the calls for democracy and against corruption of leaders, were killed around the city as the troops moved in, firing at will.
Official position
China officially maintains the protests were a “counter-revolutionary riot”.
The Chinese government said, "the “political turmoil” of 1989 was no longer relevant to today’s China. In the last three decades of reform and opening up, China’s enormous achievements in social and economic development have received worldwide attention. The building of democracy and the rule of law have continued to be perfected.”
China’s “socialism with Chinese characteristics” model was suited to “China’s national conditions and the basic interests of the vast majority.”
NOTE:
This was a significant event in China's history, hence important for GS Paper I. Not possible to cover this topic here.
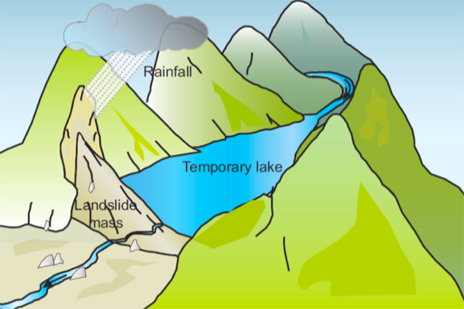
The Lahaul-Spiti local administration on Tuesday sounded a high-alert to residents of the areas downstream from the two big artificial lakes in the mountains of the tribal district’s Billing Nallah. Frequent landslides due to untimely snowfall have resulted in a blockade in the rivulet at Billing, about 400 km from the capital town.
While similar landslides had occurred in 1993 and 2001, the river discharge had soon become normalised and there was no loss to life and property, but the sudden formation of a huge waterbody could not be taken lightly at any time, he added. The snow is expected to melt in the coming days, burst the lake and lead to water discharge downhill
These lakes are also called Debris Dams, Landslide dams.
This may be useful for drug delivery, IVF and other applications at the microscopic level.
The 322 micron-long robots consist solely of a head coated in a thick cobalt-nickel layer and an uncoated tail.
China officially maintains the protests were a “counter-revolutionary riot”.
The Chinese government said, "the “political turmoil” of 1989 was no longer relevant to today’s China. In the last three decades of reform and opening up, China’s enormous achievements in social and economic development have received worldwide attention. The building of democracy and the rule of law have continued to be perfected.”
China’s “socialism with Chinese characteristics” model was suited to “China’s national conditions and the basic interests of the vast majority.”
NOTE:
This was a significant event in China's history, hence important for GS Paper I. Not possible to cover this topic here.
Artificial lakes cause alarm in Himachal’s downstream areas
While similar landslides had occurred in 1993 and 2001, the river discharge had soon become normalised and there was no loss to life and property, but the sudden formation of a huge waterbody could not be taken lightly at any time, he added. The snow is expected to melt in the coming days, burst the lake and lead to water discharge downhill
These lakes are also called Debris Dams, Landslide dams.
Sperm-inspired robots
Scientists, including one of Indian origin, have developed sperm-inspired robots controlled by oscillating weak magnetic fields.This may be useful for drug delivery, IVF and other applications at the microscopic level.
The 322 micron-long robots consist solely of a head coated in a thick cobalt-nickel layer and an uncoated tail.
Mechanism:
When the robot is subjected to an oscillating field of less than five millitesla it experiences a magnetic torque on its head, which causes its flagellum to oscillate and propel it forward. The researchers are then able to steer the robot by directing the magnetic field lines towards a reference point.
The small yet high-capacity satellites will orbit the earth at “lower altitudes than traditional satellites.”
Project Loon, a separate project by Google, is designing high-altitude balloons to provide broadband service to remote parts of the world.
When the robot is subjected to an oscillating field of less than five millitesla it experiences a magnetic torque on its head, which causes its flagellum to oscillate and propel it forward. The researchers are then able to steer the robot by directing the magnetic field lines towards a reference point.
Google funds technology to bring entire planet online
Google is planning to launch 180 satellites to provide web access to nearly 4.8 billion people (two-thirds of the world’s population) who are not yet online.The small yet high-capacity satellites will orbit the earth at “lower altitudes than traditional satellites.”
Project Loon, a separate project by Google, is designing high-altitude balloons to provide broadband service to remote parts of the world.
look at here now replica louis vuitton my website high end replica bags about his replica gucci handbags
ReplyDeletereplica bags new york anonymous h1v59x5r92 replica bags louis vuitton replica bags cheap gucci fake v9p35l1x95 replica zara bags replica prada nylon bags additional hints w2x46p2j52 replica radley bags
ReplyDelete